Learning Outcomes
Students will be able to:
i. Apply the first law of thermodynamics to analyze energy transformations in a gas undergoing reversible isothermal and adiabatic processes.
ii. Derive the equation Cp - Cv = R, where Cp represents the specific heat at constant pressure, Cv represents the specific heat at constant volume, and R is the gas constant.
iii. Explain the significance of the relationship Cp - Cv = R in understanding the behavior of ideal gases.
iv. Apply the derived equation to solve problems involving heat transfer and temperature changes in ideal gases.
Introduction
In the grand orchestra of nature, heat plays a pivotal role, driving energy transformations and shaping the world around us. The first law of thermodynamics, a cornerstone of physics, asserts that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant. This fundamental principle governs the behavior of energy in various systems and processes.
i. Delving into the Symphony of Reversible Processes
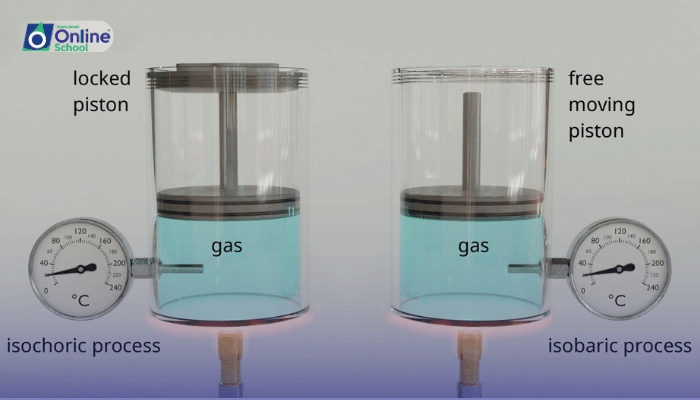
Imagine a gas undergoing a reversible isothermal process, a process where the temperature remains constant throughout. As the gas expands, it does work against the external pressure, and its internal energy decreases. This decrease in internal energy is accompanied by the absorption of heat from the surroundings.
Conversely, in a reversible adiabatic process, the gas exchanges no heat with the surroundings. As the gas expands, its internal energy decreases, and the energy lost from internal energy is converted into the work done against the external pressure.
ii. Unveiling the Relationship between Heat Capacities and the Gas Constant
By applying the first law of thermodynamics to these reversible processes, we can derive the following relationship between the specific heats (Cp and Cv) of an ideal gas and the gas constant (R):
Cp - Cv = R
where:
- Cp represents the specific heat at constant pressure, the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of a gas by one degree Celsius at constant pressure.
- Cv represents the specific heat at constant volume, the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of a gas by one degree Celsius at constant volume.
- R is the gas constant, a constant value for all ideal gases.
This equation, known as Mayer's relation, highlights the connection between the heat capacity of a gas and its behavior at constant pressure and constant volume.
iii. Applications of the Derived Equation
The relationship Cp - Cv = R has far-reaching applications in understanding the behavior of ideal gases:
Understanding Heat Transfer in Gases: The equation provides an insight into the heat transfer mechanisms in gases during various processes.
Analyzing Gas Expansion and Compression: Mayer's relation helps us analyze the energy transformations associated with gas expansion and compression, which are crucial in various applications, including engines and compressors.
Predicting Gas Behavior in Specific Conditions: The equation allows us to predict the behavior of ideal gases under specific conditions, such as constant pressure or constant volume.
The derivation of the equation Cp - Cv = R from the first law of thermodynamics is a significant milestone in understanding the behavior of ideal gases. This relationship not only provides a deeper understanding of heat transfer mechanisms in gases but also has wide-ranging applications in various fields, from engineering and chemistry to atmospheric science and beyond. As we continue to explore the universe, Mayer's relation remains a guiding principle, illuminating the path to new discoveries and advancements in our understanding of the symphony of energy that governs our world.